CNC vs. Laser: Selecting the Right Engraving & Marking Service
TL;DR
CNC engraving and marking services use computer-controlled systems to create permanent designs, text, or serial numbers on a wide array of materials. The two primary methods are mechanical CNC engraving, which physically cuts into a surface with a rotating tool, and laser engraving, which uses a focused beam of light to vaporize or alter the material. These precision services are essential for industrial part identification, commercial branding, and creating custom consumer products.
Understanding the Technologies: CNC Engraving vs. Laser Marking
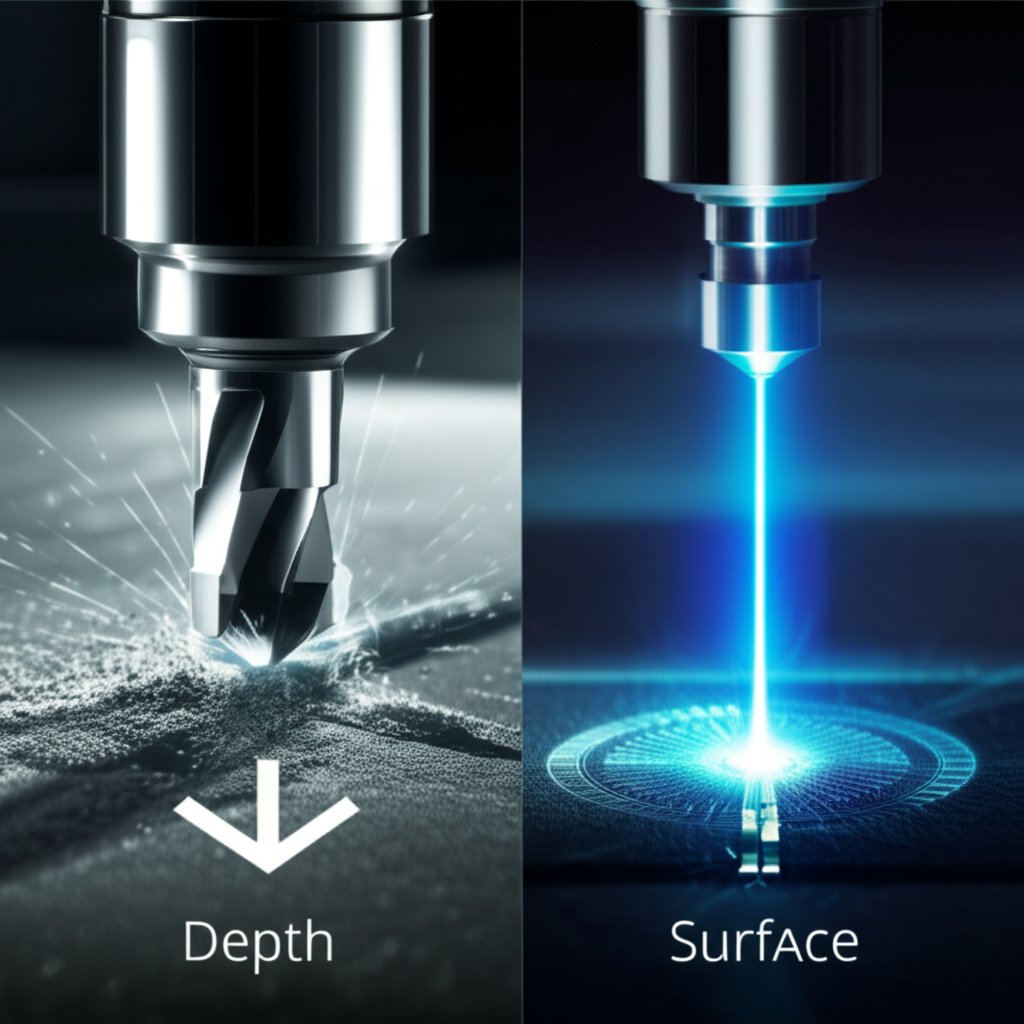
When seeking a permanent marking solution, the first critical decision involves choosing between mechanical CNC engraving and laser engraving. While both are computer-controlled for high precision, their methods and ideal applications differ significantly. Understanding these differences is key to achieving the desired finish, durability, and cost-effectiveness for your project.
Mechanical CNC engraving, also known as rotary engraving, employs a physical cutting tool, or bit, that rotates at high speeds to carve material away from the substrate. As detailed by providers like Custom Engraving Studio, this process physically removes material, creating depth and a tangible, durable mark. This method is exceptionally effective for creating deep engravings in metals and hard plastics, making it a preferred choice for industrial applications where marks must withstand harsh environments, abrasion, and wear over time.
In contrast, laser engraving uses a highly concentrated beam of light to achieve its mark. As explained by Xometry, the intense heat from the laser vaporizes the material, leaving a permanent mark on the surface. Different types of lasers, such as CO2 and Fiber lasers, are optimized for specific materials. Laser engraving excels at creating incredibly fine details, intricate patterns, and high-contrast surface marks without making physical contact with the material. This makes it ideal for delicate items, complex logos, and materials like wood, leather, and glass.
The choice between these technologies often comes down to the material, the required depth of the mark, and the level of detail. Mechanical engraving provides depth and resilience, while laser engraving offers superior precision for detailed surface designs.
| Feature | Mechanical CNC Engraving | Laser Engraving/Marking |
|---|---|---|
| Process Type | Subtractive; a rotating tool physically cuts the material. | Ablative; a focused laser beam vaporizes or alters the surface. |
| Best Materials | Metals (aluminum, steel, brass), hard plastics, wood. | Wood, acrylic, glass, leather, coated metals, some plastics. |
| Achievable Depth | Deeper grooves, often from 0.001" to 0.030". | Typically surface-level, though deep engraving is possible. |
| Precision/Tolerance | High precision with tight tolerances on location and depth. | Extremely high precision for fine details and complex graphics. |
| Common Applications | Industrial part marking, serial numbers, deep logos, signage. | Personalized gifts, promotional items, detailed logos, barcode creation. |

A Guide to Engravable Materials
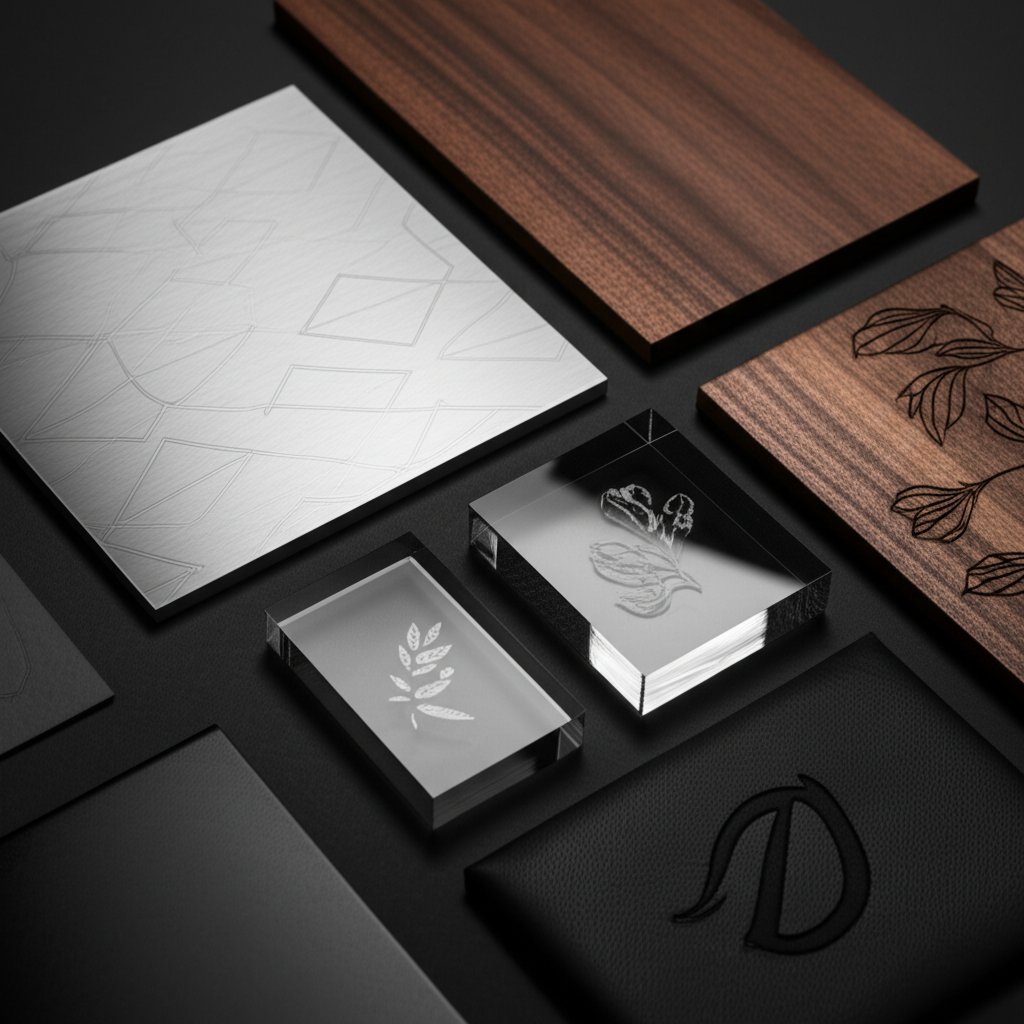
The versatility of CNC and laser services is largely defined by the vast range of compatible materials. Each material interacts differently with engraving tools and lasers, influencing the final appearance, durability, and suitability for various applications. Selecting the right material is as crucial as choosing the right engraving technology.
Below is an overview of common materials and their engraving characteristics:
- Metals: A primary category for engraving services. Aluminum, stainless steel, and brass are frequently used. Mechanical CNC engraving excels at creating deep, permanent marks for industrial traceability. Fiber lasers are highly effective for surface marking metals, creating high-contrast annealing marks or shallow etches for logos and serial numbers.
- Plastics: Materials like acrylic, ABS, and polycarbonate are widely used. Laser engraving is particularly effective on acrylic, producing a clean, frosted finish. Mechanical engraving is often used for harder plastics to create functional components, signs, and nameplates.
- Wood: A popular choice for decorative and personalized items. Laser engraving on wood creates a rustic, burned-in appearance by vaporizing the surface material. The depth and color of the mark can be controlled by adjusting the laser's power, making it ideal for photos, text, and intricate designs on items like cutting boards, plaques, and furniture.
- Leather: Laser engraving is the preferred method for leather, as it creates a debossed effect with high precision. This is commonly used for personalizing wallets, belts, patches, and other leather goods with detailed logos or text without damaging the surrounding material.
- Glass & Stone: Lasers can create a beautiful frosted effect on glass and etch into stone surfaces like marble or granite. This is often used for awards, commemorative plaques, and decorative glassware. Mechanical diamond drag engraving can also be used for fine-line etching on glass.
When planning a project, consider the material's end environment. For outdoor signage or industrial parts exposed to chemicals, a deeply engraved metal part will offer superior longevity compared to a surface-marked plastic one. For high-detail aesthetic products, the precision of a laser on wood or leather may be the better choice.
Common Applications and Industries Served
CNC engraving and marking services are integral to a multitude of industries, providing solutions that range from purely functional to highly aesthetic. The ability to create permanent, precise marks makes these technologies indispensable for traceability, branding, and personalization across various sectors.
Applications can be broadly grouped into three main categories:
- Industrial and Manufacturing: This is a primary driver for CNC engraving. In sectors like aerospace, automotive, and medical, part traceability is often a regulatory requirement. Engraving provides permanent serial numbers, part numbers, barcodes, and logos that can withstand harsh operating conditions. As noted by service providers like Universal Marking Inc., CNC engraving can hold extremely tight tolerances, which is critical for marking precision-engineered components.
- Commercial and Retail: Businesses use engraving to enhance branding and create durable products. This includes everything from custom interior and exterior signage to branded promotional items like pens, keychains, and drinkware. The high-quality finish of an engraved logo conveys a sense of permanence and quality that printing cannot match.
- Personalization and Artistic: The rise of e-commerce and custom goods has fueled demand for personalized products. Laser engraving is widely used to create custom gifts, awards, trophies, jewelry, and decorative items. The technology allows for one-of-a-kind creations, empowering artists and small businesses to offer unique products to consumers.
Ultimately, the core value of engraving lies in its permanence. Unlike labels that can peel or ink that can fade, an engraved mark becomes part of the object itself. This makes it the ideal solution for any application where durability, quality, and precision are paramount.

How to Select the Right Engraving Service Provider
Choosing the right partner for your engraving needs is critical to ensuring a successful outcome. With options ranging from local shops to large online platforms, it's important to evaluate providers based on a clear set of criteria that align with your project's specific requirements. A thorough evaluation will save time, reduce costs, and result in a higher-quality finished product.
For those engaged in product development, a partner offering integrated solutions can be invaluable. For instance, companies specializing in formative manufacturing, such as XTJ's comprehensive formative manufacturing services, can provide high-quality rapid prototypes with expert Design for Manufacturability (DFM) feedback, ensuring your design is optimized before full-scale production begins.
When selecting a provider, consider the following key factors:
- Technology and Equipment: Does the provider have the right machine for your material and design? A shop specializing in laser engraving wood may not be the best fit for deep-marking stainless steel parts. Inquire about their specific capabilities, including machine size, which dictates the maximum part dimensions they can handle.
- Material Expertise: A provider with deep experience in your chosen material will understand how to achieve the best results, avoiding common pitfalls like melting, cracking, or discoloration. Ask to see samples of their work on similar materials.
- Precision and Tolerances: For industrial applications, the ability to hold tight tolerances is non-negotiable. Ask about their quality control processes and the specific location and depth tolerances they can guarantee, which are often specified in standards like MIL-STD-130.
- File Requirements and Quoting Process: Most professional services, such as eMachineShop, require vector art files (like AI, DXF, or EPS) for engraving. A smooth process begins with clear file submission guidelines and a transparent quoting system. Understand their turnaround times and shipping options, especially when comparing local shops to national online platforms.
To prepare for a quote, follow these steps:
- Finalize your design in a vector file format.
- Clearly specify the material, including its thickness and any special finishes.
- Define the quantity of parts to be engraved.
- Indicate the precise location, size, and required depth of the engraving.
- Communicate any specific industry standards or quality requirements.
By preparing this information in advance, you enable a provider to give you an accurate quote and a clear project timeline, setting the stage for a successful partnership.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What file format do I need for CNC engraving?
Most CNC and laser engraving services require a vector-based file format to ensure the highest quality and accuracy. Common and preferred file types include DXF (Drawing Exchange Format), AI (Adobe Illustrator), EPS (Encapsulated PostScript), and SVG (Scalable Vector Graphics). These formats allow the machines to follow a precise path without losing resolution, unlike raster image files like JPG or PNG.
2. How deep can CNC engraving go?
The depth of mechanical CNC engraving can be precisely controlled and typically ranges from a shallow 0.001 inches to a deep 0.030 inches or more, depending on the material and the cutting tool used. This makes it ideal for creating durable marks that can withstand abrasion and painting. Laser engraving is typically shallower, but specialized deep laser engraving can also achieve significant depth on certain materials.
3. Is CNC engraving or laser engraving more expensive?
The cost depends heavily on the project's complexity, material, and volume. Laser engraving is often faster for complex surface designs, which can make it more cost-effective for large batches of smaller items. Mechanical CNC engraving may be more economical for simpler, deeper marks or when the setup time is minimal. It is always best to get a quote from a service provider based on your specific design and requirements.





