Medical Device CNC Machining: Processes and Standards

TL;DR
Medical device CNC machining is a high-precision, automated manufacturing process essential for creating critical components with extreme accuracy. This technology enables the production of complex parts like surgical instruments, orthopedic implants, and custom medical devices from specialized, biocompatible materials. Its core benefits—precision, consistency, and material versatility—are vital for ensuring patient safety and meeting stringent regulatory standards.
The Critical Role of CNC Machining in Modern Medical Manufacturing
Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining is a cornerstone of the modern medical industry, providing a method to fabricate complex components with unparalleled accuracy. Within the medical context, CNC machining refers to an automated process where computer-controlled machines cut, shape, and finish parts based on a digital design, such as a CAD model. This technology is indispensable for producing devices that demand the highest levels of precision, as even the slightest deviation can have significant consequences for patient safety and treatment efficacy. The ability to achieve tight tolerances and perfect repeatability across thousands of units is a primary reason for its widespread adoption.
The importance of this precision cannot be overstated. Medical components, from a tiny bone screw to a custom hip implant, must meet exact specifications to function correctly and safely within the human body. As detailed in insights from Dassault Systèmes, CNC machining delivers the consistency needed to reduce the risk of complications during medical procedures. Surgeons rely on instruments that are perfectly sharp, ergonomically sound, and flawlessly reliable—qualities that CNC technology consistently provides. This high fidelity from design to final product ensures that every device performs as intended, a non-negotiable requirement in healthcare.
Furthermore, CNC machining's versatility with materials allows manufacturers to use the most appropriate substances for specific applications, including metals, plastics, and composites. This flexibility is crucial for developing innovative devices that are both durable and biocompatible. The process also facilitates rapid prototyping, allowing engineers to quickly create and test new designs, which accelerates the pace of medical innovation. By ensuring components are optimized for fit, function, and safety before mass production, CNC machining helps bring safer and more effective medical advancements to market faster.
Key Applications: From Surgical Instruments to Life-Saving Implants
The applications of CNC machining in the medical field are vast and varied, touching nearly every aspect of patient care. The technology's ability to produce intricate, high-precision parts makes it ideal for manufacturing a wide range of devices where failure is not an option. These applications can be broadly categorized into surgical tools, orthopedic implants, and components for advanced medical equipment, each demanding unique specifications and materials.
Surgical and Handheld Instruments
Precision is paramount for tools used in surgery. CNC machining is used to manufacture a variety of surgical instruments, including scalpels, forceps, retractors, biopsy cutters, and ligation devices. As noted by Owens Industries, these tools often feature complex geometries and require exceptionally sharp, durable edges. The process ensures that each instrument is identical and meets the high standards required for clinical use, contributing to successful surgical outcomes. Customization is also a key benefit, allowing for the creation of specialized tools tailored to specific procedures or surgeon preferences.
Orthopedic and Dental Implants
CNC machining plays a critical role in producing life-changing orthopedic and dental implants. Items like hip and knee replacements, spinal implants, and bone screws must fit a patient's anatomy perfectly to ensure comfort, stability, and long-term success. According to DATRON, CNC technology is commonly used for these applications because it can precisely machine biocompatible materials like titanium and stainless steel into patient-specific shapes. This level of customization improves treatment outcomes and enhances the patient's quality of life.
Components for Advanced Medical Equipment
Beyond implants and instruments, CNC machining is essential for creating components for sophisticated medical machinery. This includes parts for pacemakers, MRI and CT scanners, diagnostic equipment, and drug delivery systems. These devices contain intricate parts that must function flawlessly to provide accurate diagnostics and reliable therapy. The ability to rapidly prototype and produce these complex components is crucial. For companies needing specialized parts, providers like XTJ offer rapid prototyping and volume production for over 30 materials, meeting demanding specifications for various industries, including medical and aerospace.
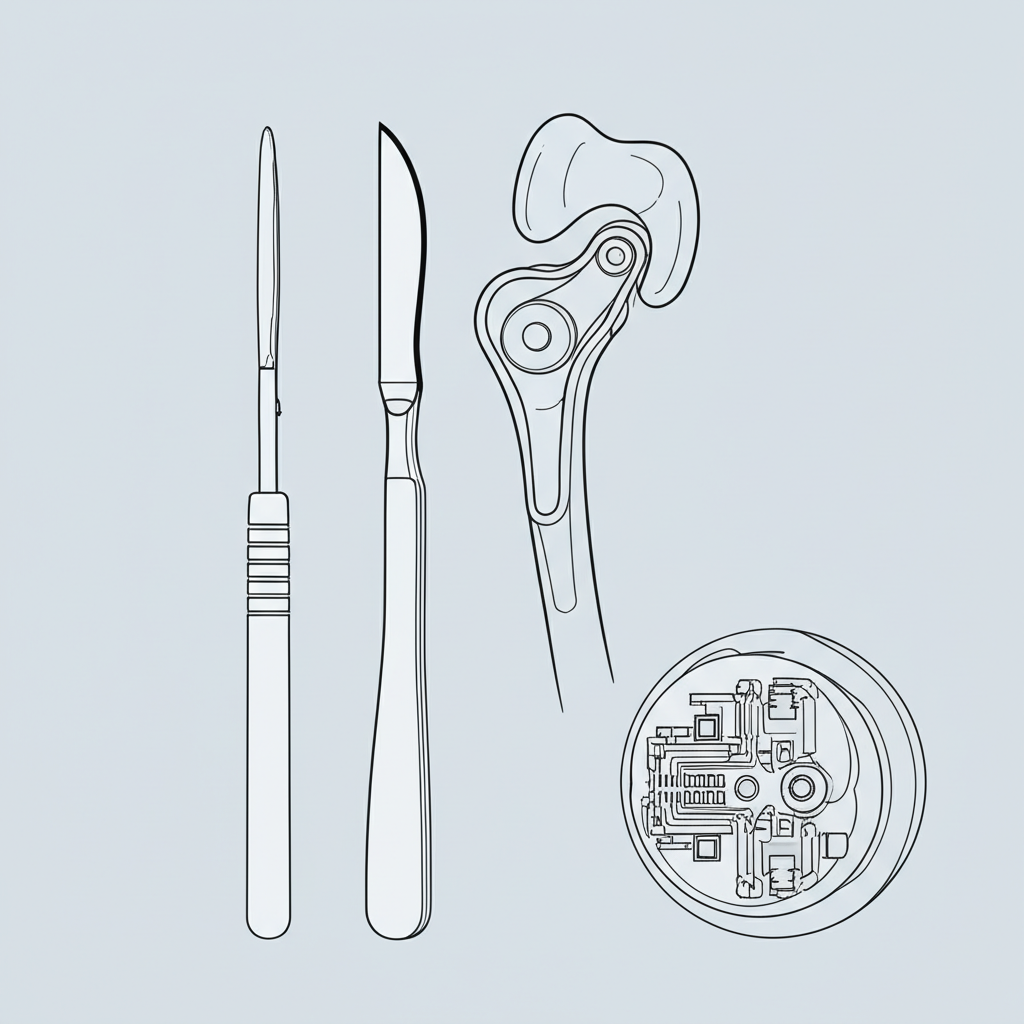
Essential Materials and Biocompatibility Considerations
Material selection is a critical aspect of medical device CNC machining, as the chosen substance must not only meet mechanical performance requirements but also be safe for human contact. The primary consideration is biocompatibility—the ability of a material to perform its desired function without eliciting a harmful local or systemic response from the body. Materials must also often withstand rigorous sterilization processes, resist corrosion from bodily fluids, and maintain their structural integrity over the device's intended lifespan.
Metals are widely used for their strength, durability, and proven track record. Titanium and its alloys are favored for implants like bone screws and joint replacements due to their high strength-to-weight ratio, excellent corrosion resistance, and elasticity that closely resembles bone. Stainless steel is another common choice, particularly for surgical instruments, because it is easily machined and sterilized. Other metals like cobalt-chrome alloys are also used for their wear resistance in high-stress applications such as artificial joints.
In addition to metals, advanced medical-grade plastics and polymers have become increasingly important. PEEK (Polyether Ether Ketone) is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and ability to be sterilized repeatedly without degradation. It is often used for spinal implants and other structural components. Other polymers and composites are selected for their specific properties, such as flexibility for catheters or transparency for diagnostic device housings. The ability of CNC machines to handle this diverse range of materials is key to modern medical manufacturing.
| Material | Key Properties | Common Medical Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Titanium (e.g., Ti-6Al-4V) | High strength-to-weight ratio, excellent biocompatibility, corrosion resistance | Orthopedic implants, bone screws, dental implants, pacemaker cases |
| Stainless Steel (e.g., 316L) | High strength, corrosion resistance, easily sterilized, cost-effective | Surgical instruments, guide pins, fixation plates |
| PEEK | High mechanical strength, radiolucent (transparent to X-rays), sterilizable | Spinal fusion cages, trauma fixation devices, dental healing caps |
| Cobalt-Chrome Alloys | Excellent wear resistance, high strength, corrosion resistance | Hip and knee joint replacements, dental bridges |

Navigating Quality Standards: ISO 13485 and FDA Registration
In the high-stakes field of medical device manufacturing, adherence to strict quality and safety standards is not optional—it is a fundamental requirement. Two of the most critical benchmarks in the industry are ISO 13485 certification and registration with the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). For any company seeking a CNC machining partner, verifying these credentials is a crucial step in the vetting process, as they provide assurance that the manufacturer operates under a robust quality management system designed specifically for medical devices.
ISO 13485 is an international standard that outlines the requirements for a quality management system (QMS) for organizations involved in the design, production, installation, and servicing of medical devices. Unlike more general quality standards like ISO 9001, ISO 13485 is tailored to the medical industry's unique demands, with a strong emphasis on risk management, process validation, and traceability. A manufacturer with this certification has demonstrated that their processes are documented, controlled, and consistently capable of producing safe and effective products. This includes everything from material sourcing and handling to machining processes and final inspection.
In the United States, medical device manufacturers must also comply with FDA regulations. This typically involves registering their establishment with the FDA and listing the devices they produce. The FDA's Quality System Regulation (21 CFR Part 820) sets forth current good manufacturing practices (cGMP) that manufacturers must follow. These regulations are legally binding and cover all aspects of production, from facility controls to equipment maintenance and personnel training. Working with an FDA-registered CNC machining shop ensures that the components are produced in a facility that is subject to FDA oversight and adheres to the stringent safety and quality controls mandated by U.S. law, providing a critical layer of trust and reliability.
Your Questions About Medical CNC Machining Answered
1. What is CNC in medical devices?
In the context of medical devices, CNC (Computer Numerical Control) refers to a highly precise and automated manufacturing process. It uses computer-programmed instructions to control machine tools like mills, lathes, and grinders to fabricate components from materials such as titanium, stainless steel, or medical-grade plastics. As explained by SYIL, this technology is essential for creating complex, high-tolerance parts for surgical instruments, implants, and diagnostic equipment, ensuring the consistency and accuracy required for patient safety.
-
Posted in
biocompatible materials, cnc machining, iso 13485, medical devices, precision manufacturing





